Papilloma of the throat is one manifestation of an infectious disease caused by human papillomavirus. Refers to the benign cuticles.
Causes of papillomas on the neck
There is one etiological reason why papilloma begins to grow on the neck or other areas of the human body - papillomavirus (HPV) infection, which is a member of the Papovaviridae family. There are more than 100 serotypes of this pathogenic substance, each of which is responsible for the appearance of another clinical picture of the disease (papilloma, condyloma, warts - these terms are synonymous, different names are related to the specificity of the location in a particular area).
The main routes of transmission are contact tubes and the genitals (condylomas in the perianal region). The virus only enters the skin in the presence of severely damaged or open wounds, in other cases it is unable to overcome the protective barrier of the skin.
Bacteria Information
- It is widespread regardless of gender (although it is more common in women than men), age or region (according to some sources, 2/3 of the world is infected with this virus).
- Contains a double-stranded, twisted ring DNA capable of adapting to the human genome.
- Infection with some strains is a high risk of cancer, especially in the case of permanent injuries. Throat papillomas are caused by a non-carcinogenic virus.
- A virus goes through two main stages of the division process. In the first stage it is in episomal (free) form, and during the same period it becomes the main division of the virus particle. This phase is reversible (after treatment there is a long-term projection). In the second stage - adaptation - the virus enters the genome of the cell (the first step towards cell transformation and the formation of a malignant tumor). The first phase is temporary and passes relatively quickly, but the second is mysterious and explains the presence of carriers.
- The base layer of the epidermis, where the virus multiplies, is affected. In the remaining layers, the bacterium may persist but not divide. Provided that the virus is in the bacterial layer, as it grows, the normal differentiation of cells in all layers of this region is disrupted, especially at the injection site level.
- Tends to cause long-term asymptomatic transport in the body (from a few months to a year). It is seldom possible to identify a specific time of infection - this is why treatment is started in the age of severe clinical manifestations, but not at the first vague symptoms.
- To prevent infection, dual and quadruple vaccines are used which are particularly effective against most carcinogenic strains 16 and 18.
Predictive Features
- Lack of hygiene. As the virus is able to maintain vital activity in the external environment for a long time, it is necessary to carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene when visiting public places (swimming pool, bathhouse, fitness center).
- Skin injuries. Minor cracks or scratches on the skin (for example due to rubbing the neck with a collar on the shirt) are enough for the virus to enter.
- Impaired immune function. Immune deficiencies of any genus create favorable conditions for the development of infections. For example, frequent colds and infectious diseases lead to a weakening of the immune system and the appearance of papillomas on the skin.
- Self-infection when scratching the skin.
- Systematic lifestyle disorder (stress, lack of exercise, improper diet). These factors affect the work of all metabolic processes in the body and lead to a reduction in the inhibitory function of the skin.
- Environmental factors affecting the reduction of the body's defenses (hypothermia, excessive ultraviolet exposure).
External manifestation of the disease
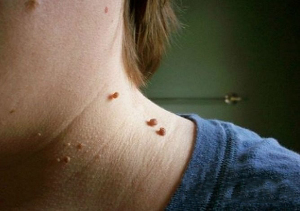
Cervical papillomas in the picture look like this:
- The growth is usually located on a broad base and stands significantly above the surface of the skin. Less frequently, the base of the papilloma is represented by a thin foot (in this case, the formation takes a hanging position). In the latter case, the risk of injury is much higher.
- The boundaries of education are equal and clear.
- The color does not differ from the surrounding skin. In rare cases, it may be a little paler or darker than the surrounding tissue.
- The surface is often even, smooth. Sometimes growth is possible at the top of the papilloma, which makes its surface torn.
- Diameter varies greatly - from 1-3 mm to a few centimeters (small diameter papillomas are more common).
- Position in any area of the neck (back, front). Sometimes the face comes into play.
Generally, many wounds are located along the skin folds.
In rare cases, papillomas of the throat can become malignant, that is, degenerating into skin tumors. This may be due to an infection with a carcinogenic HPV strain.
Signs that may indicate malignant transformation are as follows:
- color change and heterogeneity (diversity);
- boundary change (fog, loss of definition);
- asymmetrical appearance (when a line is drawn through the conditioned center of the formation two equal halves cannot be obtained);
- intensive growth;
- bleeding or ulceration (non-specific symptom, as it is also characteristic of a simple tumor on the tumor);
- itching, burning, flaking;
- dropouts are formed (small daughter formations around the central one).
The appearance of such signs does not necessarily mean the degeneration of the papilloma, but it does mean that you need to see a doctor and undergo a differential diagnosis, to find out if we are talking about a common swollen mole or skin cancer.
How to get rid of sore papillomas
Treatment of papillomas in the throat is carried out only in a complex way with a simultaneous effect on the pathological focus on the skin and on the bacterium itself in the blood.
There are several ways to fight:
Method |
Description |
Medication |
The use of cytotoxic drugs, immunosuppressants is designed to suppress copies of the virus in the affected area and reduce its concentration in the blood. Some keratolytics are applied topically directly to destroy the growth of the skin (whitening and causing tissue necrosis). |
Physical Methods |
Cryodestruction, solvent treatment, coagulation. They aim to get rid of papillomas in both the neck and other parts of the body. These methods allow you to restore the aesthetic appearance of open areas and remove the viral pool - the synthesis of the skin itself, but they do not completely remove the virus from the body. |
Combination therapy |
Combines two previous options and is therefore the most effective. |
Treatment of papillomas with home treatment (celandine juice, for example) is ineffective and often dangerous, in any case it is a prerequisite for consultation with a doctor.
Physical methods of destruction
Images can be effectively reduced by the following physical methods:
Method |
Description |
Local action with concentrated acid solutions |
1. 5% solution of zinc chloropropionate in 50% 2-chloropropionic acid, a combination of nitric acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid, lactic acid and copper nitrate trihydrate and so on. . . . The material is applied to a point with a spatula until the color of the formation changes to lighter (as soon as this has happened, further use should be stopped immediately). To completely cure papilloma, you need to do 1-2 treatments. |
Power outage |
Using a special electric knife, a spot incision is made without affecting the underlying tissue (there is a minimal effect on healthy skin cells). The method is most convenient when the formation has a long stem and small. |
Cryodestruction |
The focus is on liquid nitrogen, too low a temperature leads to tissue necrosis. It is good to clean this way of education with a broad foundation. The time of nitrogen action is chosen by a specialist (1-5 minutes). After moxibustion, incineration occurs which heals for an average of 10 days. |
Laser Removal |
The most modern and delicate approach to removing growth in prominent places such as the neck. Has the most positive reviews. With the help of fiber optics from 5 sec to 3 min in continuous mode, they work on the focus. The healing period is much shorter than with other methods (5-7 days). The technology is associated with minimal injury to nearby tissues due to the high precision of the operation. |
Classical surgery (scalpel incision) |
Rarely used, only with major damage or suspected malignancy. The reason is that the damage is often many, scattered around the neck and too small for the cut, in addition, scars can be left after surgery, which in itself creates cosmetic defects. |















































































